1. Introduction: From Data-Driven to AI-Driven
A fundamental shift is underway in enterprise intelligence. For decades, traditional analytics has been a backward-looking discipline, focused on static reporting that describes past events. Today, a new paradigm is emerging: AI-driven analytics, which is forward-moving, proactive, and predictive. Artificial intelligence is reshaping analytics from a process that explains what happened into a discipline that anticipates what will happen next, enabling dynamic and even autonomous decisions.
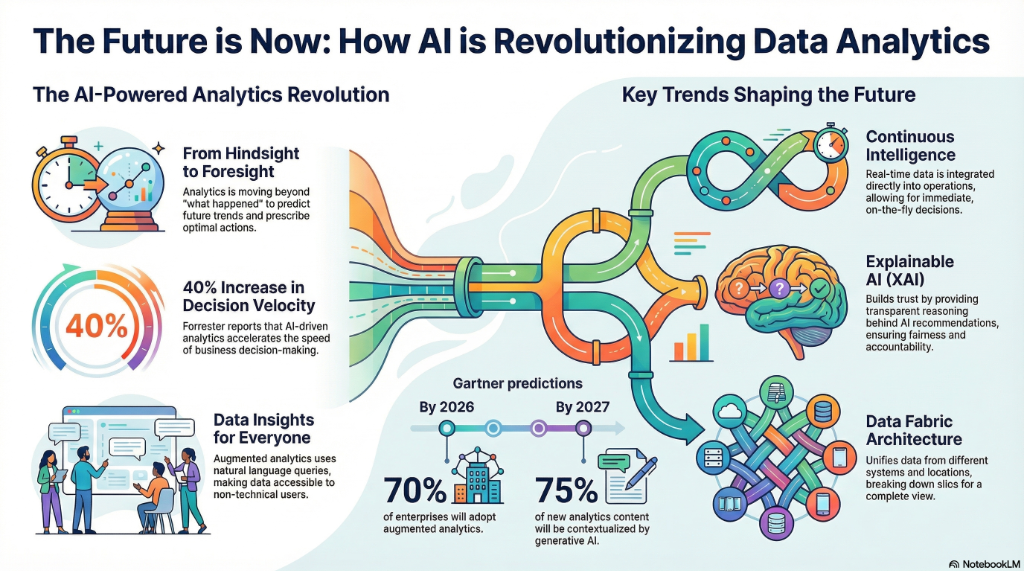
The gap between data and decision is closing, powered by AI-driven systems that can think, learn, and act with intent. We are moving from hindsight to foresight, where insight becomes anticipation. For business leaders, this is not a technological evolution to observe, but a strategic realignment to master. The winners of the next decade will be those who redesign their organizations around a core of intelligent automation, turning data from a resource into an autonomous decision-making engine.
The AI-Powered Analytics Revolution: Key Trends and Predictions Shaping the Future
2. Key Shifts Shaping the Future of Analytics
Several interconnected trends are accelerating the evolution from traditional business intelligence to an AI-powered future. Together, these trends are paving the way for what Gartner calls "perceptive analytics"—a state where analytical systems are proactive, connected, contextual, and continuous.
- Augmented Analytics: The integration of AI, machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) to streamline and automate data processing and analysis. Its primary impact is the democratization of data insights, making data-driven decision-making accessible across the entire organization.
- Continuous Intelligence: The integration of real-time analytics directly into daily business operations, enabling companies to make immediate, on-the-fly decisions based on live data streams from sources like IoT devices and transactional systems.
- Autonomous and Agentic Analytics: Analytics is evolving beyond human augmentation toward full autonomy. Agentic AI describes systems composed of specialized, independent agents that handle specific tasks and collaborate to complete complex, multi-step workflows. According to Gartner, augmented analytics capabilities will evolve into autonomous analytics platforms by 2027, which will fully manage and execute 20% of business processes.
- Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: While predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future outcomes, prescriptive analytics recommends specific actions to influence those outcomes. An emerging trend is "X Analytics," which incorporates AI to analyze all types of data—including unstructured text, audio, and video.
3. Core Capabilities of Next-Generation AI Analytics
The shift to an AI-driven model is powered by a new set of core capabilities that automate complexity, uncover deeper insights, and connect analysis directly to business outcomes:
- Automated Data Preparation and Management: AI automates the time-consuming tasks of data cleaning, quality assurance, and integration. Data preparation can consume between 45% and 80% of a data analyst's time; automation frees them for higher-value strategic work.
- Deep Learning and Pattern Recognition: Deep learning uses multi-layered neural networks to automatically learn from raw data, uncovering intricate trends and patterns in massive datasets that would be impossible to identify through basic analysis.
- Personalized Customer Insights: AI can analyze vast customer datasets—including purchase history, preferences, and unstructured data like social media comments—to create detailed consumer profiles, enabling hyper-personalization.
- Anomaly and Fraud Detection: By identifying patterns and anomalies in real-time, AI allows businesses to detect potential risks, fraudulent activities, and system vulnerabilities with greater speed and accuracy.
- Decision Intelligence and Simulation: Decision intelligence is a practical discipline that shifts the focus from being data-driven to being decision-centric. AI aids in scenario planning by simulating different potential scenarios and prescribing the best course of action.
- Enhanced Data Visualization and Storytelling: The future is moving beyond static dashboards toward more interactive and narrative-driven forms of data visualization, making complex data understandable and actionable for non-technical stakeholders.
4. Enterprise Architecture for the AI-Driven Era
Harnessing these advanced capabilities requires a modernized enterprise architecture designed for agility, scale, and intelligence. The goal is to create a dynamic "central nervous system" for the enterprise, where insights are generated, communicated, and acted upon with minimal friction.
- Data Fabric: An architecture that provides a unified, seamless view of data from multiple disparate sources, regardless of whether they are on-premises or in the cloud, essential for breaking down data silos.
- Semantic and Metadata Layers: Effective metadata management provides critical business context to technical data, enabling natural language queries and ensuring AI models produce relevant insights.
- Composite AI and Model Layers: Modern architectures embrace Composite AI, which orchestrates multiple, specialized AI techniques to solve complex business problems, supported by pre-built, customizable AI models.
- Decision Intelligence and Agentic Engines: This layer connects insights directly to actions, automating closed-loop business outcomes and utilizing AI agents to autonomously make decisions and execute workflows.
- Conversational Interfaces: The consumption of analytics is shifting from dashboards to natural language, allowing any user to query data and receive insights through simple, chat-based interactions.
5. Unlocking Business Value and Competitive Advantage
The adoption of AI-driven analytics delivers tangible business value and a significant competitive edge. Organizations that successfully integrate these capabilities are seeing measurable improvements:
| Business Outcome | Evidence and Examples |
|---|---|
| Increased Operational Efficiency | UPS dynamically adjusts delivery routes, saving over 10 million gallons of fuel annually. |
| Reduced Waste and Optimized Inventory | Walmart implemented a data fabric to unify its supply chain, leading to a 20% reduction in food wastage. |
| Enhanced Customer Engagement | PepsiCo used data storytelling to enhance marketing campaigns, resulting in a 10% improvement in customer engagement. |
| Improved Decision Velocity and Accuracy | A Forrester study found AI-driven analytics increases decision velocity by nearly 40%. McKinsey found 25% higher accuracy in insight generation. |
| Proactive Risk Mitigation | Capital One automated data governance processes, reducing compliance risks. JPMorgan Chase harnesses AI to detect fraud in real-time. |
| Accelerated Research & Development | Google's DeepMind (AlphaFold) predicted protein structures in days, a process that previously took years, accelerating drug discovery. |
6. The Evolving Role of the Analytics Professional
Contrary to common fears, AI is not replacing data analysts. Instead, it is reshaping their role, elevating them from manual data processors to strategic business partners. A recent survey found that 82% of analysts believe AI will enhance their roles, not eliminate them.
The new dynamic is a collaboration between AI and human analysts. AI excels at automating routine tasks like data cleaning and preparation, freeing humans to focus on higher-value activities that require critical thinking, strategic planning, and domain expertise. The analyst's role is shifting toward interpreting AI-generated insights, asking more strategic questions, and validating the outputs of automated systems.
A key emerging skill is "data storytelling"—the ability to weave data and visuals into a compelling narrative that makes complex insights accessible and drives business decisions. As the democratization of data allows non-technical users to access basic insights on their own, the professional analyst is elevated to focus on more complex, ambiguous, and strategic challenges that require a uniquely human touch.
7. Navigating Risks, Constraints, and Responsible AI
The transition to AI-driven analytics is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate significant risks and constraints to ensure these powerful technologies are deployed responsibly and effectively.
Ethical and Data-Related Risks
AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Algorithms trained on biased or incomplete datasets can perpetuate and even amplify existing social biases, leading to unfair outcomes. Organizations must strike a careful balance between data utilization and data privacy, ensuring all data is acquired legally and managed carefully.
Trust and Transparency
Building trust in AI-generated insights is a major hurdle. Explainable AI (XAI) has emerged as a critical response to the "black box" problem, providing transparency into how an algorithm reached a specific conclusion. XAI is not just a technical solution but a foundational requirement for addressing ethical risks and meeting regulatory demands for accountability.
Technical and Organizational Hurdles
Many organizations face significant technical challenges in integrating modern AI solutions with legacy systems. Beyond technical issues, hurdles include a shortage of skilled AI professionals and organizational resistance to change.
Governance and Regulation
The growing power of AI has led to an increasing need for robust governance and the emergence of new regulatory frameworks, such as the EU AI Act. A key risk in autonomous systems is "agent drift," where an AI's actions gradually deviate from desired outcomes. Organizations are developing "guardian agents"—specialized systems tasked with monitoring AI behavior.
8. A Roadmap for Evolving Toward AI-Driven Analytics
For organizations looking to mature their analytics capabilities, a phased approach ensures a successful transformation:
- Stage 1: Strengthen the Data Foundation - Ensure data is high-quality, reliable, and accessible. Implement a Data Fabric architecture to unify data from disparate silos. Establish effective Metadata Management to provide business context to raw data.
- Stage 2: Introduce Augmented Analytics - Deploy Augmented Analytics tools to democratize data access for business users, enabling them to get answers through natural language queries and automated insight generation.
- Stage 3: Scale Decision Intelligence and Automation - Move from insight generation to automated action. Implement Continuous Intelligence to support real-time operational decisions. Scale Decision Intelligence Platforms and Agentic AI to automate complex workflows.
9. Conclusion: The Analytics Landscape of the Next 5–10 Years
The future of data analytics is no longer about simply reporting on the past; it is about proactively shaping the future. The emerging landscape is defined by systems that are proactive, collaborative, connected, contextual, and continuous—a state of "perceptive analytics."
In the next 5-10 years, we will see AI function as a strategic partner in the C-suite, multimodal AI that understands text, images, and voice become the status quo, and agentic systems that proactively anticipate business needs and automate responses. The central theme remains one of human-AI collaboration, where intelligent systems amplify human reasoning and accelerate decision cycles far beyond what was previously possible.
The enterprises that will lead in the next decade are those that successfully combine human intent with machine precision. They will complete the journey from hindsight to foresight, transforming the overwhelming complexity of data into a clear and decisive strategic advantage that is not just predictive, but perceptive.